
LARYNGECTOMY.NET
Anatomy reminders
The aerodigestive tracts are the set of air cavities and pathways of the face and neck. It includes two pathways: the digestive tract (oral cavity, pharynx, hypo pharynx and oesophagus) and the respiratory tract (nasal cavities, pharynx, larynx and trachea).
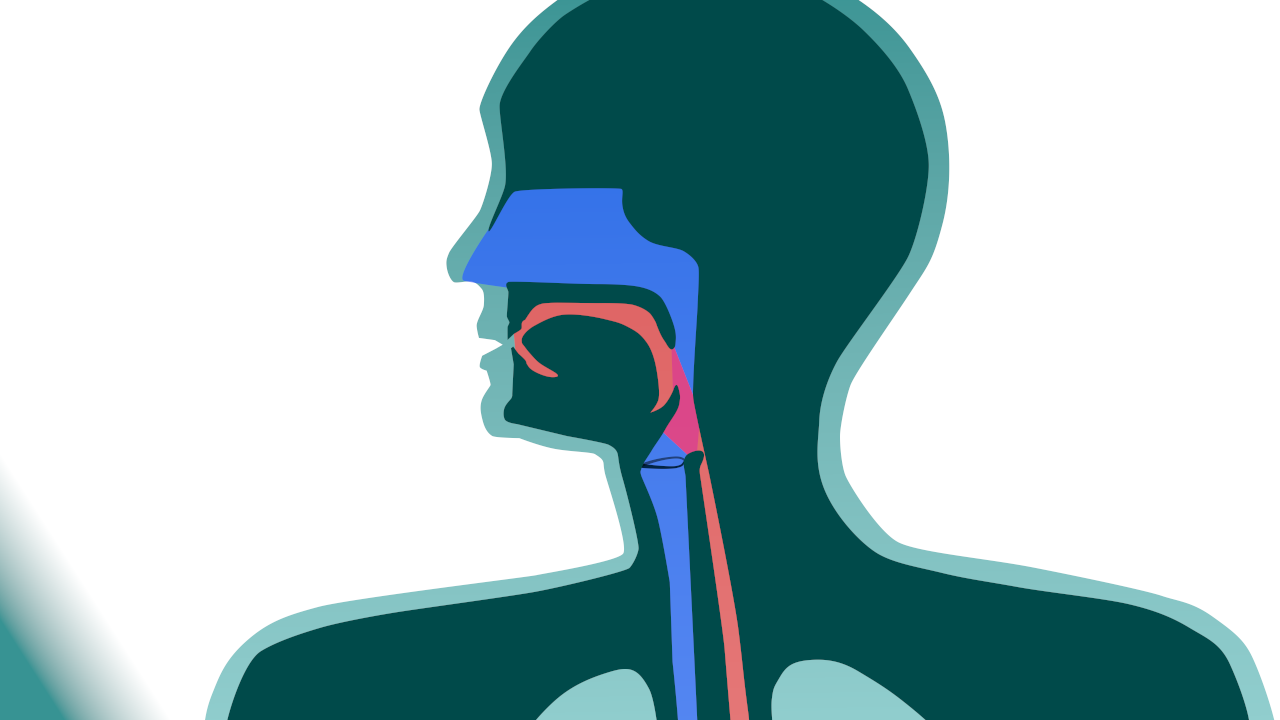
The larynx is at the crossroads of three functions: swallowing, breathing and speech.
At rest or during inspiration, the larynx ensures the passage of air towards the trachea and then to the lungs. The larynx is then in an open position.
When the larynx is closed, the respiratory pulmonary air generates vibrations in the vocal chords, the sound created is modulated and enriched by the pharyngeal-oro-nasal cavity.
The vocal chords are composed of two horizontal muscle folds which meet towards the front and may move apart or move closer one to another towards the back.
The blockage of the larynx in a closed position also allows performing certain abdominal efforts.
During swallowing, the epiglottis tilts towards the back. It prevents the food from entering the respiratory tract and sends them into the oesophagus.
Breathing before laryngectomy
Swallowing before laryngectomy
Speech before laryngectomy

